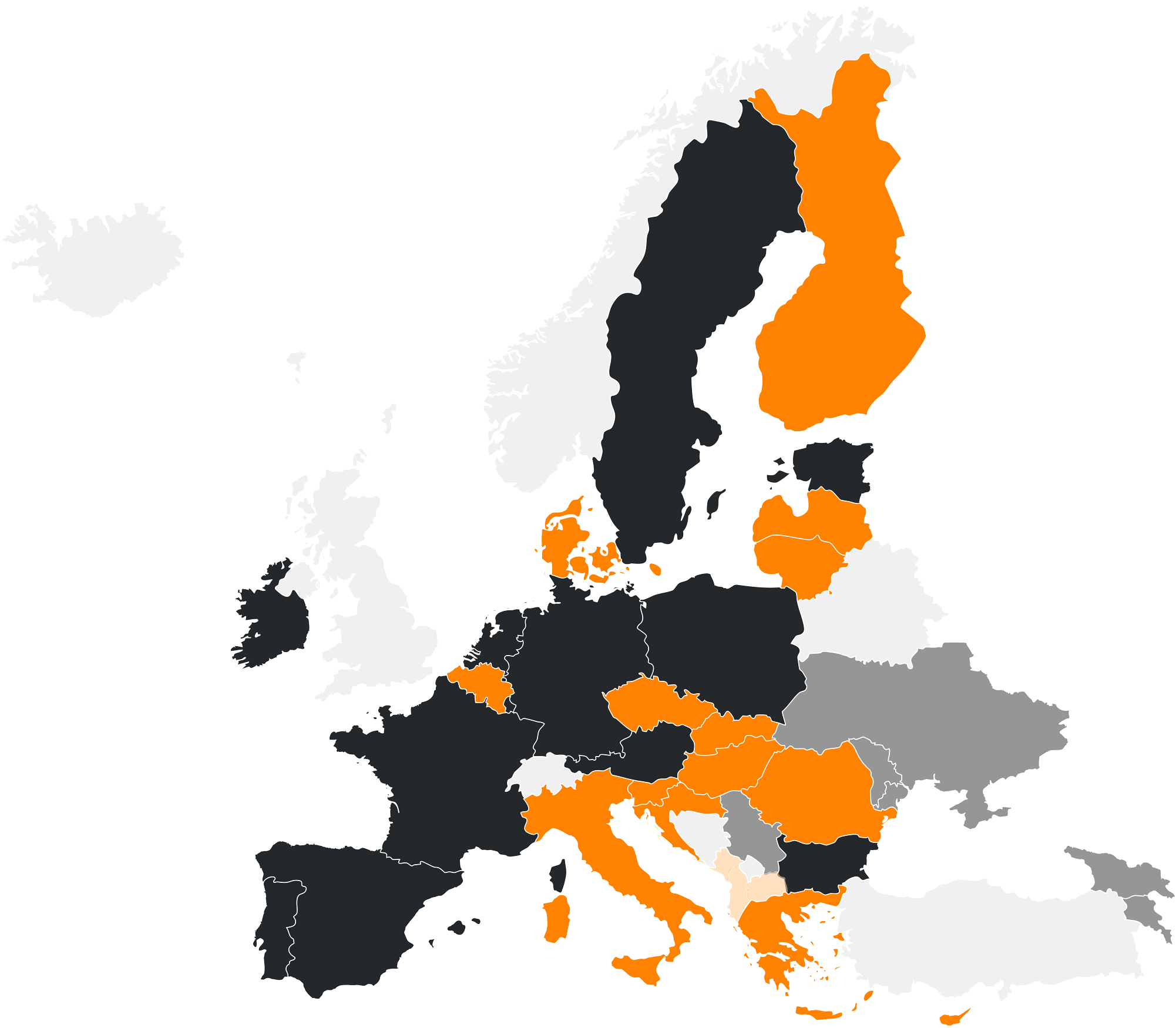
NIS2 Directive: EU Member States Transposition
The transposition of Directive (EU) 2022/2555 (“NIS2 Directive”) marks a fundamental step in strengthening the cybersecurity posture of the European Union. Each Member State has adopted its own regulatory approach, reflecting different legal traditions, supervisory models and national security priorities.
This section provides an overview of the countries that have formally implemented NIS2. For each State, a short descriptive sentence highlights the distinctive feature of its national transposition, followed by the official legislative source(s).